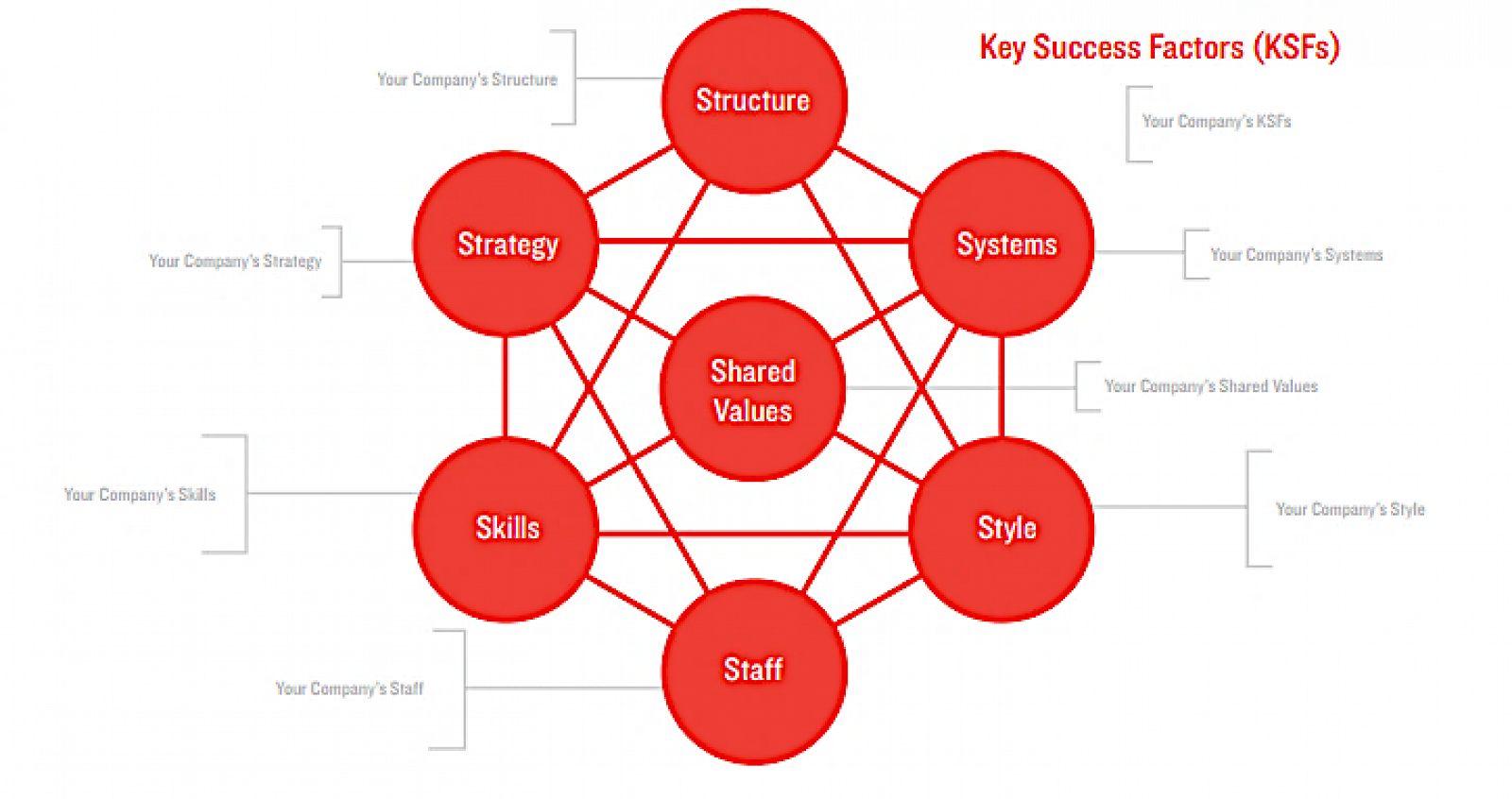
Developed by consultants at McKinsey & Co., the 7-S model posits that organisations are built on 7 ‘hard’ and ‘soft’ elements:
- The hard elements are easy to identify: Strategy, Structure and Systems
- The soft elements are difficult to identify: Style, Staff, Skills and Shared Values

The Hard Elements
A brief description:
- Strategy: The long-term direction and scope of the firm
- Structure: Reporting relationships, areas of expertise
- Systems: Formal and informal procedures for routine activities
The Soft Elements
A brief description:
- Skills: Capabilities and competencies. What do we do best?
- Shared Values: The beliefs guiding employees’ behaviour
- Staff: Methods of developing, training and motivating people
- Style: Top management’s leadership approach
What is the purpose of the 7-S?
To achieve total alignment in all 7 areas. This is also known as:
- Organisational Fit
- Goal Congruence
- Isomorphism
The 7-S Model: Achieving Fit
Effective leaders find the right balance between the 7 elements. A change in one element affects the others. For example:
- New IT Systems influence Staffing and Skilling
- In turn, Staffing and Skilling influence Performance Expectations
An Example: Accenture

The 7-S Model: KSFs
Key Success Factors are:
- The outcomes that the organisation must deliver to achieve or exceed desired goals.
- They are usually a shortlist of 3-5 functions, activities or processes
- They may be weaknesses that need to be overcome to deliver on growth.

For example, possible KSF’s for Snapchat are:
- To simplify the user interface, making it easier to use
- To increase the number of active users
- To attract the older demographic
- To increase advertising revenue
- To enhance share price and shareholder value
The 7-S Blank Canvas